Lesson 1: Describe cloud computing
1.1 Define cloud computing
Cloud computing: delivery of computing services over the internet.
Computing services include: virtual machine (VM), storage, databases, networking, Internet of Things (IoT), ML and AI.
Because cloud computing uses the internet to deliver these services, doesn't have to be constrained by phyical infrastructure, such as datacenter → can use the cloud to rapidly expand your IT footprint.
1.2 Describe the shared responsibility model
Responsibility of the cloud provider: Physical security, power, cooling and network connectivity
Responsibility of the consumer: Data and information stored in the cloud, access security (only give access to those who need it).
Ex) Cloud SQL DB
- The cloud provider is responsible for maintaining the actual DB, but customer still responsible for the data that gets ingested into the DB.
- If you deployed a VM and installed SQl DB on it, you are still responsible for DB patches and updates, maintaining the data stored in the DB.
With on-premises datacenter, customer is responsible for everything, but with cloud computing , the responsibilities shift.
The shared responsibility model is tied into cloud service types:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): places the most responsibility on the consumer and cloud provider responsible for the basics of physical security, power, and connectivity.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): places the most responsibility with the cloud provider
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): in the middle
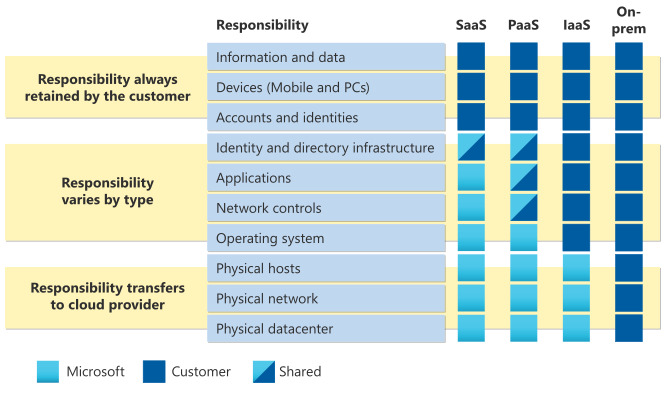
Customer always responsible for:
- info and data stored in the cloud
- devices that are allowed to connect to the cloud (cell phones, computers, ...)
- accounts and identities of the people, services, and devices within your organization
Cloud provider always responsible for:
- physical datacenter
- physical network
- physical hosts
Your service model determines the responsibility of the following:
- OS
- Network controls
- Applications
- Identity and infrastructure
1.3 Define cloud models
The cloud models define the deployment type of cloud resources.
Private Cloud
Private cloud: cloud (delivering IT services over the internet) that's used by a single entity.
Private cloud provides much greater control for the company but comes with greater cost and fewer of the benefits of a public cloud deployment.
Private cloud can be hosted on your datacenter, or by a third party.
Public Cloud
A public cloud is built, controlled, and maintained by a third-party cloud provider.
With a public cloud, anyone that wants to purchase cloud services can access and use resources.
The general public availability is a key difference between private clouds and public clouds.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid computing is a computing environment that uses both public and private clouds in an inter-connected environment.
A hybrid cloud environment can be used to allow a private cloud to surge for increased, temporary demand by deploying public cloud resources.
Hybrid cloud can be used to provide an extra layer of security.
Ex) Users can flexibly choose which services to keep in public cloud and which to deploy to their private cloud infrastructure.
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
| No capital expenditures to scale up | Organizations have complete control over resources and security | Provides the most flexibility |
| Applications can be quickly provisioned and deprovisioned | Data is not collected with other organizations' data | Organizations determine where to run their applications |
| Organizations pay for what they use | Hardware must be purchased for startup and maintenance | Organizations control security, compliance, or legal requirements |
| Organizations don't have complete control over resources and security | Organizations are responsible for hardware maintenance and updates |
Multi-Cloud
Multi-cloud: you use multiple public cloud providers (use different features from different cloud providers).
Azure Arc
Azure Arc is a set of technologies that helps manage your cloud environment, whether it's a public cloud solely on Azure, a private cloud in your datacenter, a hybrid configuration, or in a multi-cloud environment.
1.4 Describe the consumption-based model
Two types of expenses in IT infrastructure models:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): One-time, up-front expenditure to purchase or secure resources, e.g. building a datacenter
- Operational Expenditure (OpEx): Spending money on services or products over time, e.g. cloud services (you pay for the IT resources you use)
OpEx consumption-based model has benefits:
- No upfront costs
- No need to purchase and manage costly infrastructure that users might not use to its fullest potential
- The ability to pay for more resources when they are needed
- The ability to stop paying for resources that are no longer needed
Compare Cloud pricing models
Cloud compting is the delivery of computing services over the internet by using a pay-as-you-go pricing model. You pay only for the cloud services you use, which helps you:
- plan and manage your operating costs
- run your infrastructure more efficiently
- scale as your business needs change
Module Assessment
1. What is cloud computing?
Delivery of computing services over the internet
2. Which cloud model uses some datacenters focused on providing cloud services to anyone that wants them, and some data centers that are focused on a single customer?
Hybrid cloud - The hybrid cloud model is a combination of public cloud and private cloud, using both datacenters dedicated solely to one customer and datacenters that are shared with the public
3. According to the shared responsibility model, which cloud service type places the most responsibility on the customer?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
'회사 > Azure AZ-900 자격증 준비' 카테고리의 다른 글
| AZ-900 자격증 준비 6 - Describe Azure storage services (3) | 2025.06.23 |
|---|---|
| AZ-900 자격증 준비 5 - Describe Azure compute and networking services (1) | 2025.06.17 |
| AZ-900 자격증 준비 4 - Describe the core architectural components of Azure (0) | 2025.06.17 |
| AZ-900 자격증 준비 3 - Describe cloud service types (0) | 2025.04.04 |
| AZ-900 자격증 준비 2 - Describe the benefits of using cloud services (0) | 2025.04.04 |




댓글